From Traditional Wet-Lab to AI-Powered XDC Development
Over the past two years, the ADC market has been experiencing rapid growth: there are now 200+ ADCs in clinical development globally, with around 15 approved drugs. The market is projected to reach $14–16 billion by 2025, as the industry expands from ADCs to PDCs and RDCs.
At the same time, drug R&D challenges are shifting. Today's bottleneck is no longer whether efficacy is strong enough, but whether the therapeutic window can be controlled in a stable and predictable way. AI is becoming a key lever for improving R&D certainty, and the paradigm of drug discovery is evolving accordingly.
As a leading CXO in the industry, Viva Biotech recognized this trend early and has systematically evolved its R&D workflow by integrating wet-lab capabilities to AI-powered design. At the heart of this transformation is our “Technology Platform + Algorithm” model, which delivers unique value at every critical stage of XDC development. Our core competitiveness stems from deep integration across two dimensions:
Platform Integration
Our biologics, small-molecule, peptide, and computational teams are all centralized, comprising over 1,000 researchers. This physical concentration generates synergistic effects far beyond conventional operations. From AI design to molecular synthesis, antibody expression, conjugation reactions, analytical characterization, in vitro evaluation, and PK/PD studies, all departments operate in a highly coordinated closed loop. This allows AI-designed concepts to be rapidly converted into experimental data, with feedback seamlessly integrated back into algorithmic optimization.
Algorithm Integration
After years of practice, we have established end-to-end AI design capabilities covering antibodies, peptides, linkers, and small-molecule payloads, gradually progressing toward fully integrated XDC molecular design. Compared with the traditional linear workflow,we upgraded to an approach that simultaneously optimizes multiple factors from the outset, including PK, tissue distribution, stability, DAR distribution, hydrophobicity, and cellular internalization efficiency.
Deepening Conjugation Technologies: From Established Methods to Precision Design
If XDC drug development is likened to building a highly sophisticated molecular machine, conjugation technology is the critical process that assembles its individual components. Viva Biotech has established a systematic capability spanning from well-validated classical methods to frontier, innovation-driven approaches.
A Solid Foundation for Non-specific Conjugation Methodologies
Viva Biotech has established a robust R&D infrastructure characterized by rigorous quality control protocols. This framework ensures high-fidelity batch-to-batch reproducibility and maintains exceptional process stability across conventional development workflows.
Controlled Site-Specific Conjugation
Site-specific conjugation enables precise control of antibody ratio (DAR). By evaluating the interaction between payload hydrophobicity and the surface characteristics of specific antibodies, we identify optimal conjugation sites and linker–payload combinations. This results in a more stable and predictable relationship between critical quality attributes and in vivo performance, enabling tighter process control and more rational clinical dose optimization.
Intelligent Design Case Studies in Site-specific Conjugation
· Dual-payload conjugation
By delivering two payloads with complementary mechanisms on a single antibody, this strategy enables synergistic efficacy, mitigates resistance risk, and expands the treatable patient population. In complex tumor microenvironments or settings with low or heterogeneous antigen expression, dual-payload conjugation broadens cytotoxic coverage while increasing effective dose density without elevating systemic exposure.
· Bridge conjugation
This approach involves selectively opening interchain disulfide bonds and reconnecting them using specialized linkers, achieving conjugation while reconstructing and stabilizing the disulfide bridges. The result is preserved antibody conformation, thermal stability, and colloidal stability, while reducing heterogeneity risks such as chain dissociation or residual free thiols commonly associated with random conjugation. The design and synthesis of these specialized linkers are carried out by our small-molecule platform, followed by conjugation by dedicated teams and comprehensive characterization by analytical groups. This seamless end-to-end integration ensures high fidelity from molecular design to experimental realization.
· Glycan-specific conjugation
We have advanced novel glycan-specific conjugation technologies that upgrade the traditional “two-enzyme, three-step” process to streamlined “two-enzyme, one-step” and “one-enzyme, two-step” workflows. These innovations significantly simplify the conjugation process, reduce purification steps, and lower overall costs. While maintaining reproducibility, they markedly improve conjugation efficiency and overall yield, resulting in a more robust and scalable manufacturing process.
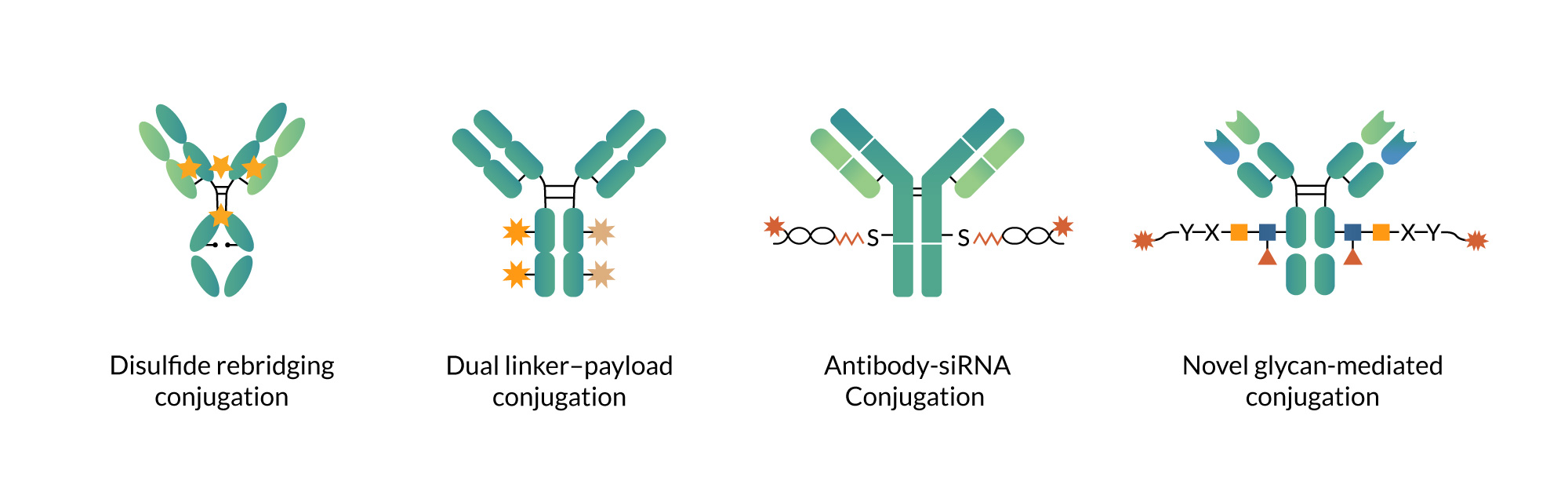
Examples of Specialized Conjugation Modalities
Beyond ADC: Expanding XDC Modalities Through Integrated Capability Building
Viva Biotech continues to build scalable development capabilities for emerging modalities, ensuring that when data shows that “a peptide may be more suitable than an antibody for a given target,” the platform can immediately translate that insight into experimentally testable solutions. For novel conjugate formats—including peptide–drug conjugates (PDCs), radionuclide–drug conjugates (RDCs), and antisense oligonucleotide conjugates (AOCs)—Viva Biotech has developed the customized, fully integrated technology platforms covering design, synthesis, conjugation, molecular characterization, and biological evaluation.
At the molecular design level, Viva Biotech's AI capabilities span small molecules, biologics, peptides, and conjugated drugs. In small-molecule design, the integration of molecular dynamics and de novo design technologies enables the exploration of novel chemical matter and innovative mechanisms of action. In biologics design, we have established comprehensive workflows for antibody humanization, affinity maturation, affinity and selectivity tuning, and patent expansion, delivering significantly improved speed and efficiency compared with traditional antibody discovery approaches. In peptide design—particularly cyclic peptides—we have built systematic development methodologies covering structural modeling, affinity optimization, cyclization strategies, incorporation of non-natural amino acids, and in silico PK property prediction. For conjugated drug design, we have developed AI-based scoring methods for site-specific conjugation optimization, enabling rapid identification of optimal conjugation sites and linker designs. These capabilities support fast, high-quality molecular design and are tightly integrated with experimental platforms to complete synthesis, conjugation, characterization, and biological evaluation in a seamless workflow.
On the wet-lab side, our peptide synthesis teams have accumulated deep expertise in challenging syntheses such as branched peptides and cyclic peptides, with proven capabilities in complex side-chain modifications, diverse cyclization strategies, and the use of non-natural amino acids with specialized protecting groups. In parallel, our peptide teams have developed extensive experience in RDC molecule synthesis, with one of the most advanced RDC programs developed through our collaborations already progressing into clinical development.
In the development of AOCs, the strong negative charge and limited stability of RNA impose stringent requirements on conjugation conditions and molecular characterization. To address these challenges, we systematically incorporate stability-enhancing modifications at the sequence design stage and apply specialized handling strategies during conjugation to prevent degradation. Moreover, due to the overall negative charge of AOCs, their analysis, purification, and structural characterization differ fundamentally from ADCs—traditional hydrophobic interaction chromatography (HIC) methods are no longer applicable, necessitating the use of ion-exchange–based analytical and purification approaches. Through these efforts, we have successfully established a complete and robust technical framework and delivered multiple high-complexity AOC programs.
End-to-End Quality Control: From “Making Molecules” to “Understanding Molecules”
If conjugation technologies enable the creation of complex modalities, rigorous quality oversight provides the mastery to understand them. It is not enough to know what a molecule looks like; we must decode why it takes that form and how this governs its biological behavior in vivo.
High-Throughput Development Platforms
Our platforms support the parallel expression and screening of hundreds of protein constructs. Combined with rapid molecular iteration and optimization, this significantly shortens the cycle from design to validation, accelerating candidate convergence and data-driven decision-making.
Multi-dimensional Quality Analytics
We integrate a complementary suite of analytical technologies, including:
· High-resolution mass spectrometry: Precise quantification of DAR species distributions
· Chromatographic methods (SEC/HIC/IEX): monitoring aggregation, hydrophobicity, and charge heterogeneity
· Peptide mapping and glycan analysis: tracking modification profiles and critical site consistency
· Stability assessments (DSF/DSC/DLS): evaluating thermal and colloidal stability
Functional Evaluation
By integrating cell-based binding and internalization assays with in vitro functional evaluations, we enable early-stage assessment of conjugation strategies and molecular architectures. This approach rapidly identifies key sources of heterogeneity and potential risks, provides quantitative guidance for candidate selection and downstream development pathways, and ensures that critical quality attributes are systematically controlled from the earliest stages of development.
Viva Biotech has established an integrated XDC development capability spanning from wet-lab to AI-powered design. This represents not merely a layering of technologies, but a fundamental paradigm shift—one that deeply integrates the collaborative strengths of the physical laboratory with the predictive power of algorithmic space. Through this integration, XDC development is transitioning from experience-driven trial to data-driven precision design. In the future, we will continue to refining our integrated design capabilities with the long-term objective of enabling end-to-end predictability, from molecular design to clinical efficacy.

