MOG35-55/MOG1-125-induced EAE in mice
MBP-induced EAE in rats
PLP139-151-induced EAE in mice
Collagen-induced arthritis (CIA) in mice and rats
Collagen antibody-induced arthritis (CAIA) in mice
Adjuvant-induced arthritis (AIA) in rats
Pristane-induced lupus in mice
MRL/lpr mice lupus model
DSS-induced ulcerative colitis in mice
TNBS-induced crohn's disease in mice
IL-10 Knockout spontaneous colitis model
CD4+CD45RBhigh T cell-induced colitis in mice
Oxazolone-induced atopic dermatitis in mice
MC903-induced dermatitis in mice
DNCB-induced dermatitis in mice and rats
FITC-induced dermatitis in mice
Imiquimod-induced psoriasis in mice
IL-23-induced ear epidermal hyperplasia in mice
OVA-induced asthma in mice
HDM-induced asthma in mice
Oxazolone-induced DTH in mice
KLH-induced DTH in mice
CCl4-induced liver fibrosis in mice and rats
DMN-induced liver fibrosis in mice and rats
TAA-induced liver fibrosis in mice and rats
Bile Duct Ligation (BDL) model in mice and rats
Bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in mice
Folic acid-induced kidney fibrosis in mice
KLH-induced TDAR in mice
OVA-induced eosinophilic gastroenteritis in mice
Carrageenan-induced air pouch in mice and rats
rhIL-13-induced air pouch in mice
GvHD induced by X-ray irradiation in mice
GvHD without irradiation in rats
-
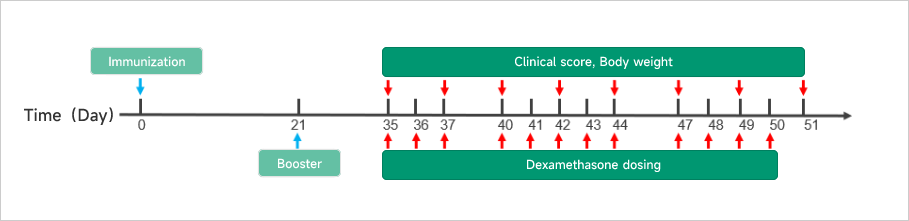
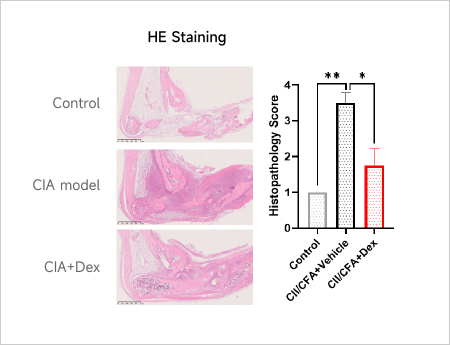
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)Case Study: Collagen-induced Arthritis (CIA) ModelAnimals: DBA/1, 7-8 weeks, maleModeling reagent: Bovine CII + CFA emulsionModeling method: Immunization: day 0, i.d., tail Booster: day 21ReadoutsClinical observation: Limb score, BWHistopathology: H&E、Synovial inflammation、Bone Erosion
 Clinical and Histological Assessment in Collagen-induced CIA Model
Clinical and Histological Assessment in Collagen-induced CIA Model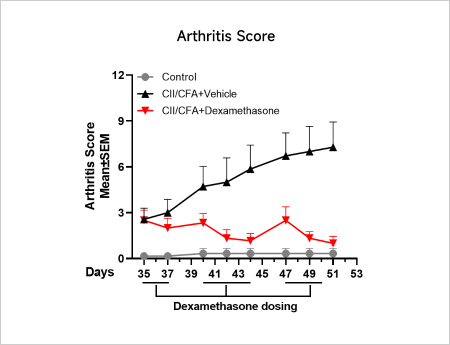
-
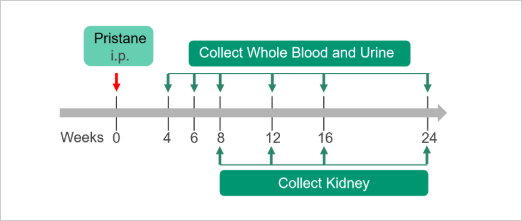
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE)Case Study: Pristane-induced SLE ModelExperimental animals: Balb/c, 6-8 weeks, femaleModeling reagent: PristaneModeling method: 0.5ml, i.p., onceReadoutsClinical observation: Body weightHistopathology: H&E、IHC or IFUrine chemistry analysis: Creatinine, UTP, mALB, UREACellular and molecular levels: Anti-dsDNA IgG 、Cytokine level 、FACS
 Anti-dsDNA Analysis in Pristane-induced SLE Model
Anti-dsDNA Analysis in Pristane-induced SLE Model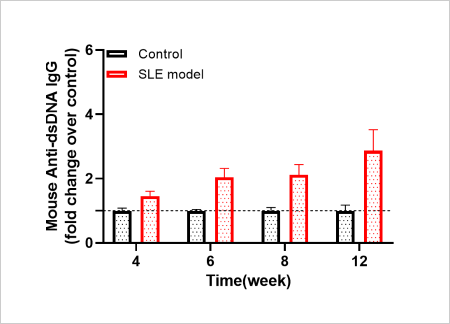
-
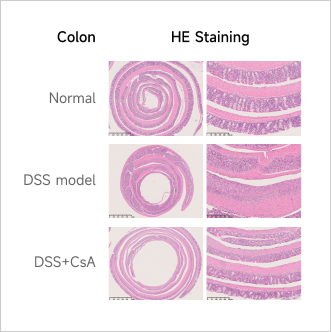
Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD)Case Study: DSS-induced Acute Ulcerative Colitis ModelExperimental animals: C57BL/6, 7 weeks, femaleModeling reagent: Dextran Sulfate Sodium (DSS)Modeling method: Free drinking water containing DSS for consecutive 7 daysReadoutsClinical observation: DAI score, BWHistopathology: Colon H&E stainingMolecular levels: Cytokine level
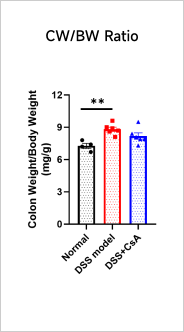
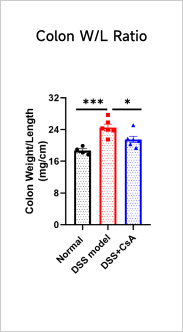
 Clinical and Histological Assessment in DSS-induced UC Model
Clinical and Histological Assessment in DSS-induced UC Model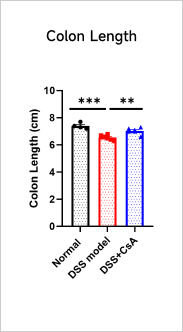
-
Atopic Dermatitis (AD)Case Study: Oxazolone-induced Atopic Dermatitis (AD) ModelExperimental animals: Balb/c, 6-8 weeks, femaleModeling reagent: Oxazolone (OXA)Modeling method: Sensitization: day 0 on back
Rechallenge: day7-21 on right ear, 7 timesReadoutsClinical observation: Ear thickness, BWHistopathology: H&E、Immune infiltrationCellular and molecular levels: FACS analysis、Cytokine level、Total IgE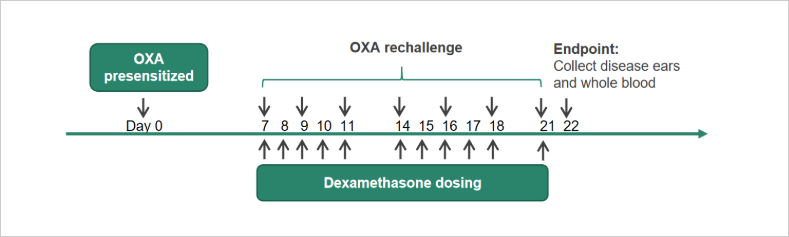 Clinical and Histological Assessment in OXA-induced AD Model
Clinical and Histological Assessment in OXA-induced AD Model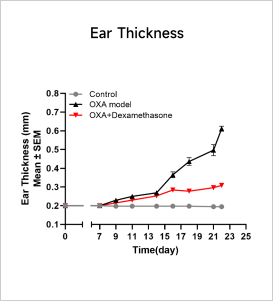
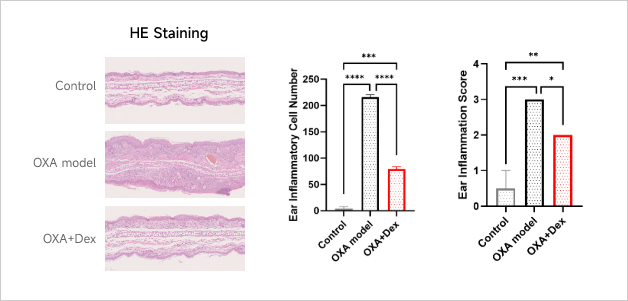 Case Study: MC903-induced Atopic Dermatitis (AD) ModelExperimental animals: C57BL/6, 7-8 weeks, femaleModeling reagent: MC903Modeling method: Topically, on ear, 8 timesReadoutsClinical observation: Ear thickness, BWHistopathology: H&E stainingCellular and molecular levels: Cytokine level、Total IgE
Case Study: MC903-induced Atopic Dermatitis (AD) ModelExperimental animals: C57BL/6, 7-8 weeks, femaleModeling reagent: MC903Modeling method: Topically, on ear, 8 timesReadoutsClinical observation: Ear thickness, BWHistopathology: H&E stainingCellular and molecular levels: Cytokine level、Total IgE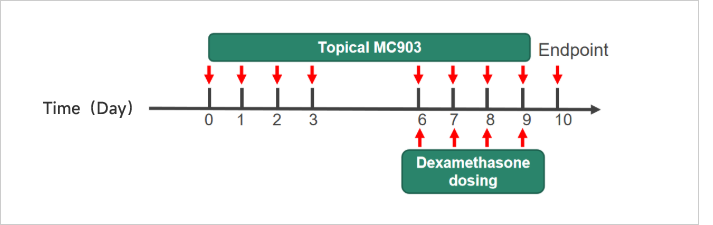 Clinical and Histological Assessment in MC903-induced AD Model
Clinical and Histological Assessment in MC903-induced AD Model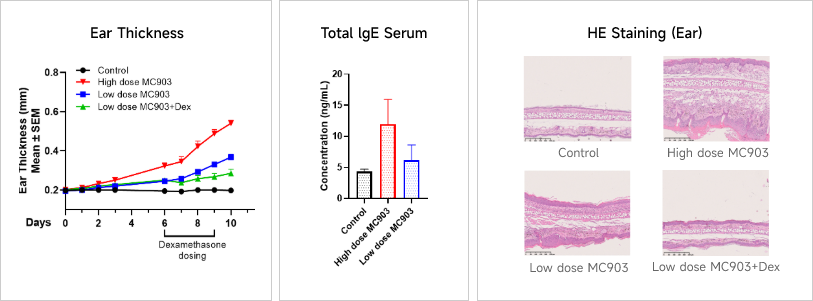
-
PsoriasisCase Study: IMQ-induced Psoriasis ModelExperimental animals: C57BL/6, 7 weeks, femaleModeling reagent: Imiquimod (IMQ) creamModeling method: Topically applicated on dorsal for consecutive 6 daysReadoutsClinical observation: Skin thickness, PASI score, BWHistopathology: H&E stainingCellular and molecular levels: Cytokine level、FACS
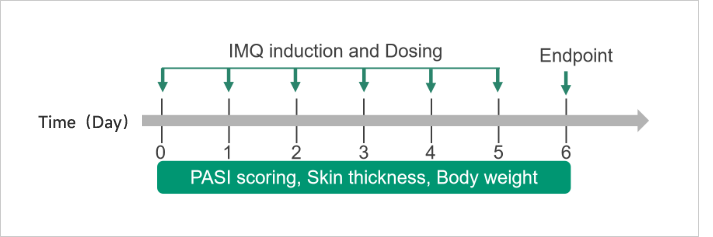 Clinical and Histological Assessment in IMQ-induced Psoriasis Model
Clinical and Histological Assessment in IMQ-induced Psoriasis Model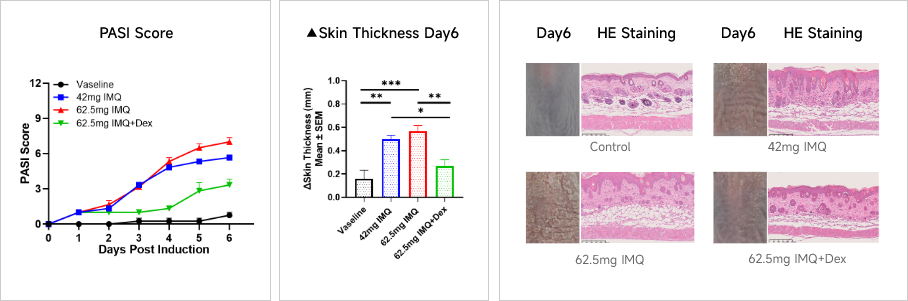 Case Study: IL-23-induced Ear Epidermal Hyperplasia ModelExperimental animals: C57BL/6, 7 weeks, femaleModeling reagent: Recombinant mouse IL-23 and human IL-23Modeling method: Intradermal injection, ear, 4 timesReadoutsClinical observation: Ear thickness, BWHistopathology: H&E stainingCellular and molecular levels: Cytokine level、FACS
Case Study: IL-23-induced Ear Epidermal Hyperplasia ModelExperimental animals: C57BL/6, 7 weeks, femaleModeling reagent: Recombinant mouse IL-23 and human IL-23Modeling method: Intradermal injection, ear, 4 timesReadoutsClinical observation: Ear thickness, BWHistopathology: H&E stainingCellular and molecular levels: Cytokine level、FACS Clinical and Histological Assessment in IL-23-induced Ear Epidermal Hyperplasia Model
Clinical and Histological Assessment in IL-23-induced Ear Epidermal Hyperplasia Model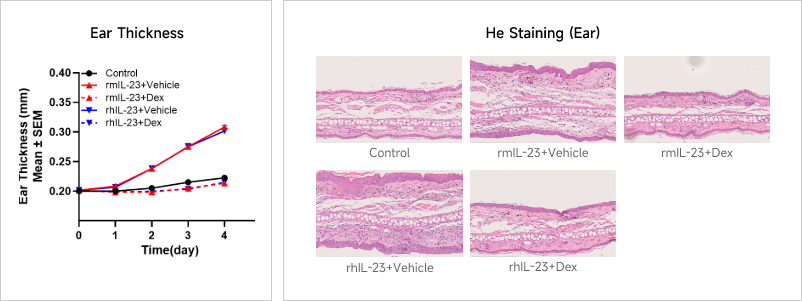
-
AsthmaCase Study: OVA-induced Asthma ModelExperimental animals:Balb/c, 6-8 weeks, femaleModeling reagent:Ovalbumin (OVA) + Al(OH)3Modeling method:Sensitization: i.p., on day 0, 7, 14 Rechallenge: Intranasal, on day21-25ReadoutsClinical observation:Body weight, Health conditionHistopathology:H&E, PAS Staining、IHCCellular and molecular levels:FACS analysis、Cytokine level、Total IgE, OVA specific IgE
 Histological Assessment in OVA-induced Asthma Model
Histological Assessment in OVA-induced Asthma Model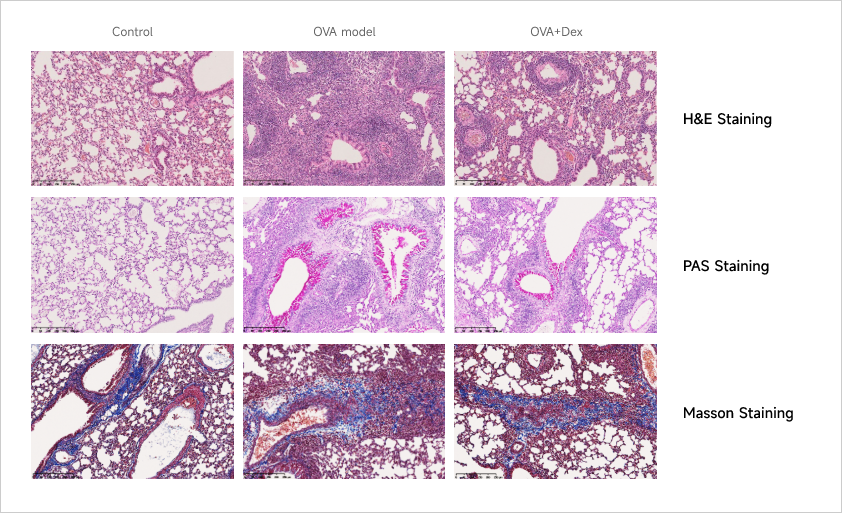
After OVA induction, there is a significant infiltration of inflammatory cells in the lung tissue, and the structure of the airway is disordered, and the normal structure of the bronchi and alveoli is damaged.
There is a significant increase in the number of goblet cells in the airway epithelium. The PAS staining highlights a large amount of mucus secretion.
Due to the experimental cycle, pulmonary fibrosis is not obvious after OVA induction.
Dexamethasone treatment ameliorates the pathological changes, including reducing goblet cell hyperplasia, decreasing mucus secretion, alleviating inflammatory cell infiltration, and improving airway and tissue architectural integrity.
Total IgE and Cytokine Analyses in OVA-induced Asthma Model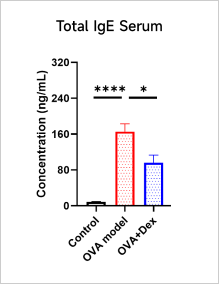
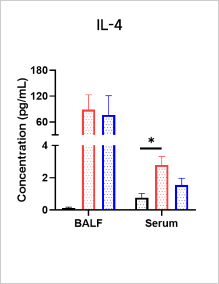
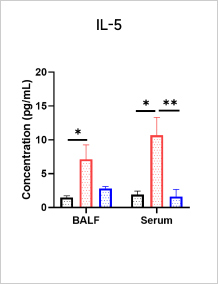
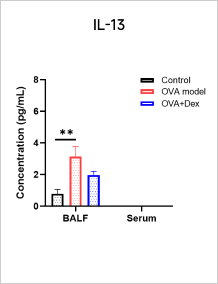
A significant increase in the level of total IgE can be observed in serum after OVA induction.
After OVA induction, the expression of Th2-type cytokines (IL - 4, IL - 5, IL - 13) is up-regulated and Dexamethasone treatment can reduce the levels of IL - 4, IL - 5, and IL-13 and total IgE.
-
Liver FibrosisCase Study: CCl4-induced Liver Fibrosis ModelExperimental animals:C57BL/6, 6-8 weeks, maleModeling reagent:CCl4/Olive oilModeling method:BIW, i.p., 8 weeksReadoutsClinical observation:Body weight, Health conditionHistopathology:H&E staining, Masson or SR staining、IHC (α-SMA)Serum biochemical:ALT, AST, TBA, ALB, ALPHistopathological Analysis in CCl4-induced Liver Fibrosis Model
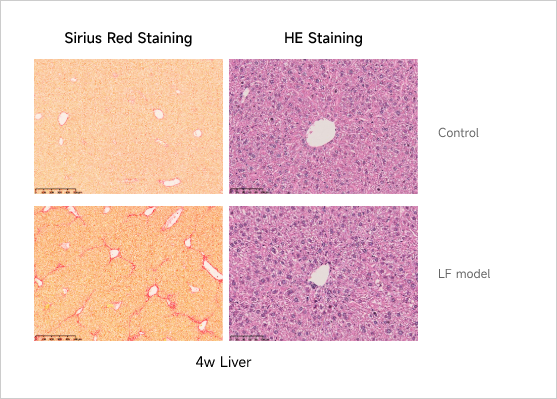
-
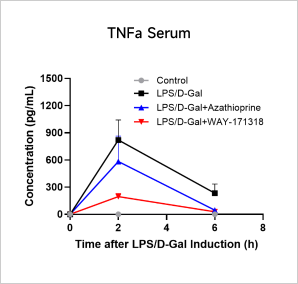
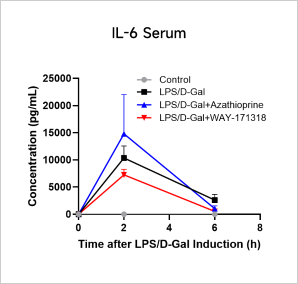
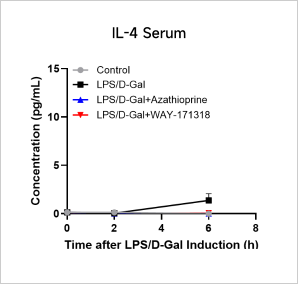
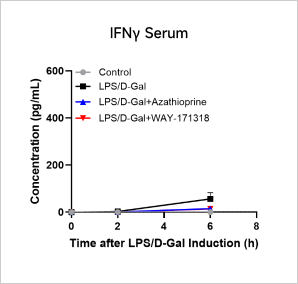
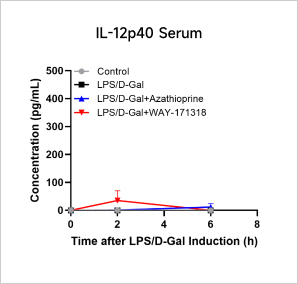
LPS-induced Acute InflammationCase Study: LPS-Induced Acute Inflammation ModelObjective:To evaluate the effect of Azathioprine and WAY-171318 in LPS-induced acute inflammation modelAnimal:C57BL/6, 6-8 weeks, femaleModeling reagent:LPS + D-GalactosamineModeling method:
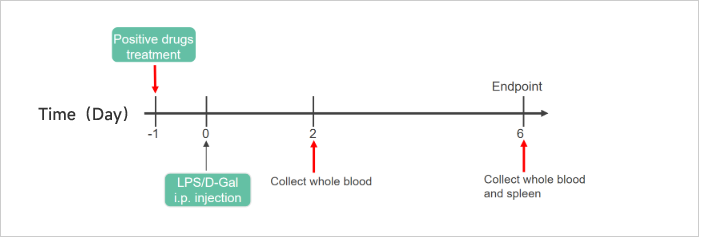 Cytokine Analyses iN LPS-Induced Inflammation Model
Cytokine Analyses iN LPS-Induced Inflammation Model