- About Us
-
CRO Services
- PROTAC/Molecular Glue Services
- Protein Preparation and Ternary Complex Structure Determination
- PROTAC/Molecular Glues Screening
- PROTAC Ternary Complex Kinetics (SPR)
- PROTAC Degradation Assays and Ternary Complex Assays
- PROTAC Molecule Design and Synthesis
- ADME & PK/PD Studies of PROTAC Molecules
- AIDD/CADD PROTAC Design
- CDMO Services
- EFS Business
- News
- Careers
- Investor Relations
- Contact Us


Recently, Viva Biotech contributed to the research published in The EMBO Journal, titled “Structural basis of Fanconi anemia pathway activation by FANCM”. The study provides important new insights into the structure and functional mechanisms of FANCM. Dr. Dongming Qian, Vice President of Bioscience at Viva Biotech, and Dr. Yin Wu, Associate Director of Bioscience at Viva Biotech, played key roles in this study. Leveraging Viva Biotech's advanced platforms for protein production and structural analysis, they successfully resolved the high-resolution crystal structures of key FANCM domains in complex with DNA, providing crucial technical support and scientific evidence for the disclosure of this structural type.

(Source: EMBO website)
FANCM is crucial in genome maintenance, functioning in the Fanconi anemia (FA) pathway, alternative lengthening of telomeres (ALT), and replication fork protection. FANCM recognizes branched DNA structures and promotes their remodeling through ATP-dependent branch migration. The protein has emerged as a promising therapeutic target due to synthetic lethal interactions with BRCA1, SMARCAL1, and RAD52, and in ALT-positive cancers. The crystal structures of FANCM's N-terminal ATP-dependent translocase domain (2.2 Å) and C-terminal FAAP24-bound region (2.4 Å), both complexed with branched DNA. Through structural analysis, biochemical reconstitution, and cellular studies, the researchers demonstrate that FANCM employs two distinct mechanisms: an ATP-dependent branch migration activity essential for DNA damage survival, and a branched DNA-binding mode that enhances FANCD2-FANCI monoubiquitination through FA core complex interaction. The N-terminal translocase domain specifically recognizes DNA junctions through multiple key elements, while the C-terminal FAAP24-binding domain engages adjacent double-stranded DNA. The study results reveal how FANCM evolved from an ancient DNA repair motor into a sophisticated sensor that couples DNA damage recognition to selective pathway activation, providing a structural framework for developing targeted therapeutics.
In this study, Viva Biotech's protein and structural biology team successfully obtained a high-resolution (2.2 Å) crystal structure of the FANCM's N-terminal ATP-dependent translocase domain complexed with DNA. This is the testament of Viva Biotech's strong recombinant protein expression and purification platform, covering E. coli, insect, mammalian, and yeast expression systems, as well as world-class crystallization and structural analysis capabilities. The structure reveals key interaction sites between the domain and DNA, shedding light on the mechanism by which FANCM participates in DNA repair. The disclosure of crystal structure fills a critical gap in the structural research of the FANCM helicase domain and provides an essential foundation for future drug discovery and development.
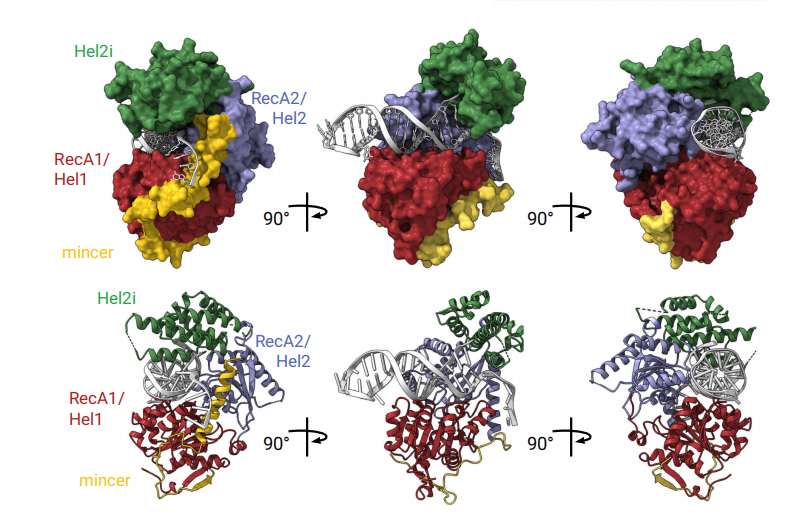
(Image source from this study; the above crystal structures were independently resolved by VivaBiotech.)
For more information, please refer to the full paper:
Rohan Bythell-Douglas, et al. “Structural Basis of Fanconi Anemia Pathway Activation by FANCM.” The EMBO Journal, 30 May 2025, https://doi.org/10.1038/s44318-025-00468-3.
A world-leading protein structure research platform

Since its founding in 2008, Viva Biotech has been deeply committed to advancing the frontiers of protein structure research, continuously raising technological standards and refining platform capabilities. Over the past 16 years, the company has successfully tackled numerous challenges in protein structure determination, earning the trust of global partners through its profound understanding of client needs and expert scientific judgment.
To learn more about our protein expression and structural biology platforms, please visit https://www.vivabiotech.com or contact our expert team at info@vivabiotech.com.
Copyright © Viva Biotech All Rights Reserved. 沪ICP备19036061号
- About Us
-
CRO Services
BackCRO ServicesService & Technology
- CDMO Services
- EFS Business
- News
- Careers
- Investor Relations
- Contact Us