Artificial Intelligence (AI) is sparking a new wave of revolution in the biopharmaceutical field with its unprecedented advantages and unlimited potential. As a world leader in structural biology, Viva Biotech has fully integrated the dry-lab and the wet-lab platforms and opened up new avenues for drug discovery. The applications of AI in the field are ubiquitous, spanning from the accurate prediction of biochemical interactions to efficient identification of promising compounds for subsequent lead optimization. In addition, the recent emergence of generative AI enables de novo design of small molecules, antibodies and other biologics, bringing novelty and complementary to conventional drug design frameworks.
Viva Biotech has established a comprehensive in-house Artificial Intelligence Drug Discovery (AIDD) and Computer-aided Drug Discovery (CADD) platform for small molecule drug discovery, offering a complete AI-driven drug discovery workflow that significantly reduces the cost and timelines and brings the drug discovery process to the next level. For example, active learning-augmented virtual screening can increase hit rates from an average of 1% to over 20%, with enrichment factors of 20 times or more. By integrating with Viva Biotech’s screening platforms, the screening and assay validation process is accelerated from months to weeks which effectively reduces the costs by two-thirds. The use of free energy perturbation (FEP) and ADMET property predictions allow for preliminary compound property assessments. The in silico-guided synthesis cuts the total number of compounds by more than a half and shortens the lead discovery cycle from 12-36 months to 6-18 months.
The integration of computational and wet-lab techniques opens up all kinds of possibilities. Viva Biotech's combination of AI and computational chemistry is advancing the development of emerging drug modalities such as RNA-targeting small molecules, peptides/cyclic peptides, and antibody drugs, as well as employing de novo design for these modalities.
FEP methods for non-covalent and covalent small molecule design
FEP is a highly accurate binding affinity calculation method that has been widely used for lead optimization. Given well-characterized starting geometries, FEP calculations with error ranges under 1 kcal/mol are routinely used to accelerate the molecular design and in turn improve the success rates. Viva Biotech's AIDD and CADD team uses quantum mechanics (QM) in conjunction with its proprietary FEP platform, which accurately captures the transitional states in covalent reactions and the corresponding energy barriers. A high correlation between the apparent free energy changes and the Kinact/Ki value is established as validated by the experiments. This method is well-suited to guide the covalent compound design and improve target selectivity, regardless of the warhead and chemical reaction types. FEP plays a crucial role in Viva's AI and computer-aided small molecule drug discovery workflow, integrating with molecular dynamics (MD) for binding site identification, high throughput virtual screening, and ADMET predictions to create a comprehensive AI-driven drug discovery ecosystem.
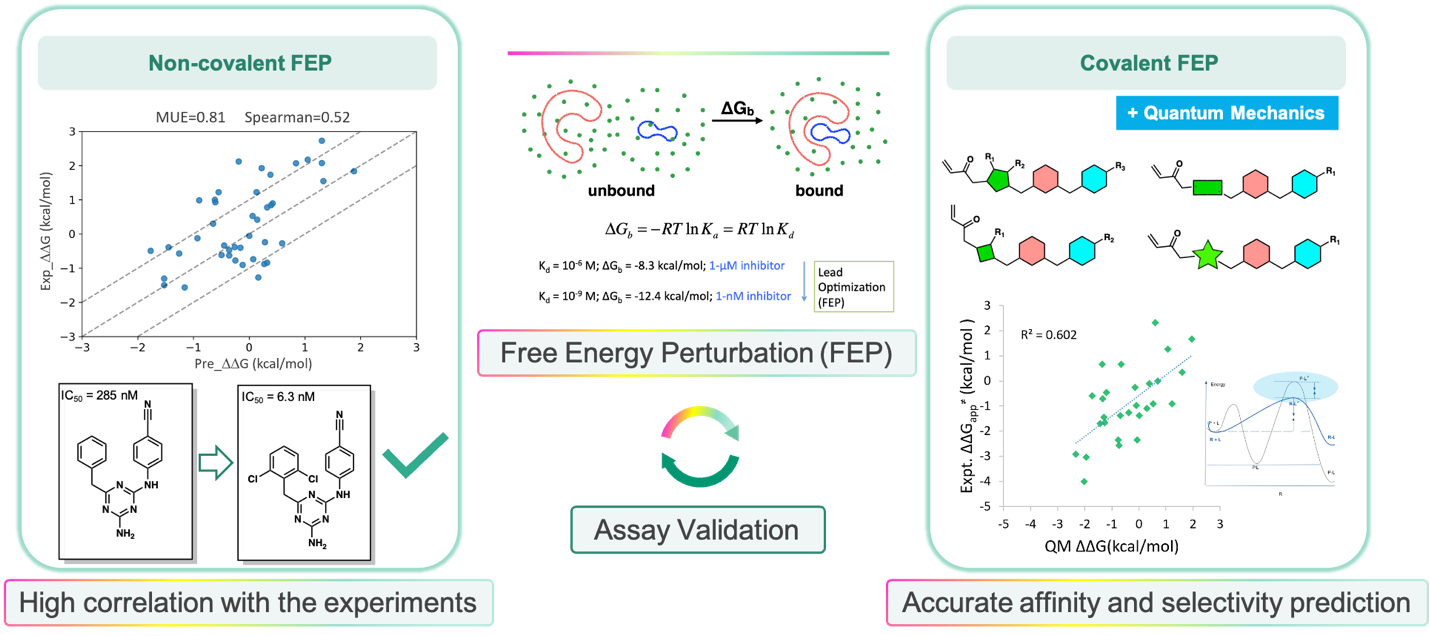
FEP for noncovalent and covalent affinity prediction
Unique AI and structure-based drug discovery (SBDD) approach for RNA-targeted small molecule design
RNA as a target has unique advantages over traditional protein targets enabling previously undruggable proteins to become druggable. Since the FDA approval of the RNA-targeting small molecule Risdiplam in 2020, such drug modality has drawn significant industry attention. Traditional methods often fail to capture the dynamic characteristics of RNA structures and are not able to predict the structural changes of the flexible and highly charged RNA under different conditions. Viva Biotech's AIDD and CADD platform has developed MD-based methods to describe these dynamic features, highlighting the RNA pocket changes in the presence of small molecules and providing a series of quantitative metrics for rational RNA-targeting small molecule design.
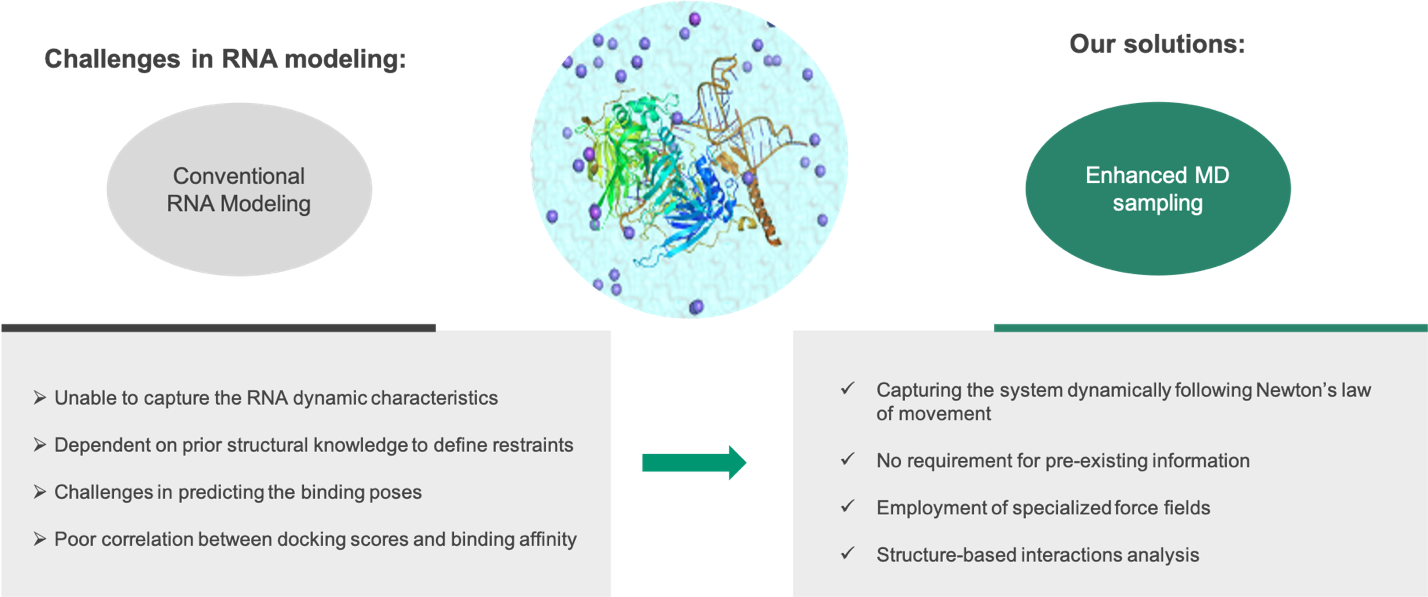
Viva Biotech uses unique MD-based algorithms to overcome the challenges of targeting RNAs
AI + DNA encoded library (DEL)-powered cyclic peptide design
Cyclic peptides are often used to target protein-protein interaction sites, offering advantages such as stability, bioavailability, and specificity. Traditional screening methods struggle with covering the vast chemical space of cyclic peptides, resulting in low hit rates and inefficient screening. At Viva Biotech, we bring out the best of AI and V-DEL screening. We first leverage structure-based modeling to enrich peptide building blocks and create focused peptide libraries with over a billion cyclic peptides. We then incorporated AIDD and CADD algorithms to optimize the cyclic peptide hits while closely monitoring their stability and membrane permeability. Such tools are used iteratively to ultimately identify high affinity and highly specific cyclic peptides.
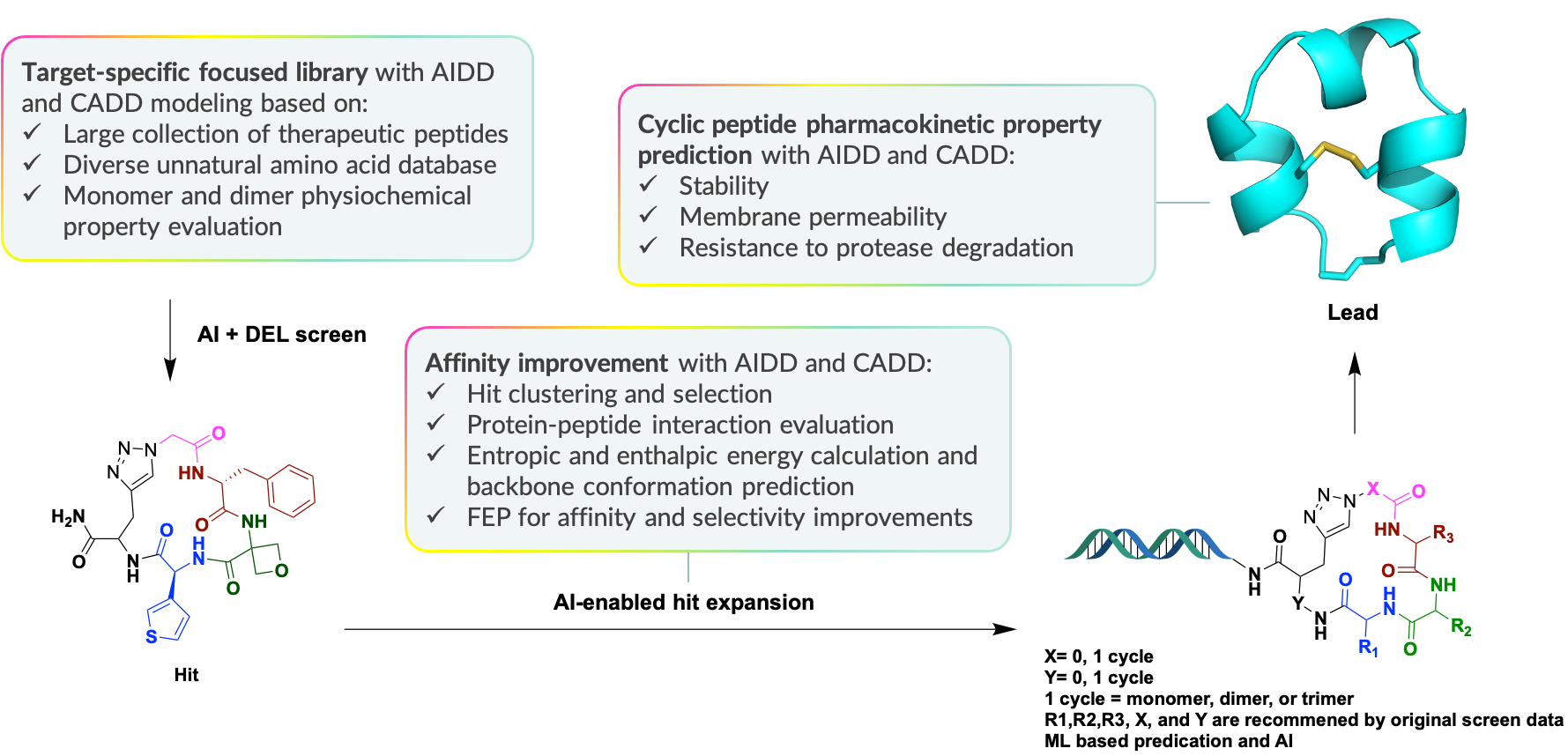
AI-focused DEL cyclic peptide screening process
New era of antibody design: Weaving AI with antibody expression and validation
Affinity maturation is crucial in antibody design. The traditional phage-display technique has long turnaround time and low efficiency. The data generated are hardly used for modeling due to the lack of negative feedbacks. The introduction of computational tools can drastically shorten the experimental cycles by explicit sequence expression and validation. In the meantime, the models are improved through multiple rounds of trials and binding measurement feedback. Such integration is now the status quo of Viva's antibody affinity maturation protocol and has achieved great success. In one case study, physics-based models and deep-learning algorithms were used to predict the antibody-antigen complex structure, followed by residue screening, in silico mutations, affinity predictions, and antibody developability index prediction. ELISA showed that out of the 20 mutants that were screened 7 sequences maintained comparable affinity and 1 showed a 4-fold affinity increase. In the second round of optimization, the computational design identified another mutant sequence with a nearly 7-fold affinity boost.
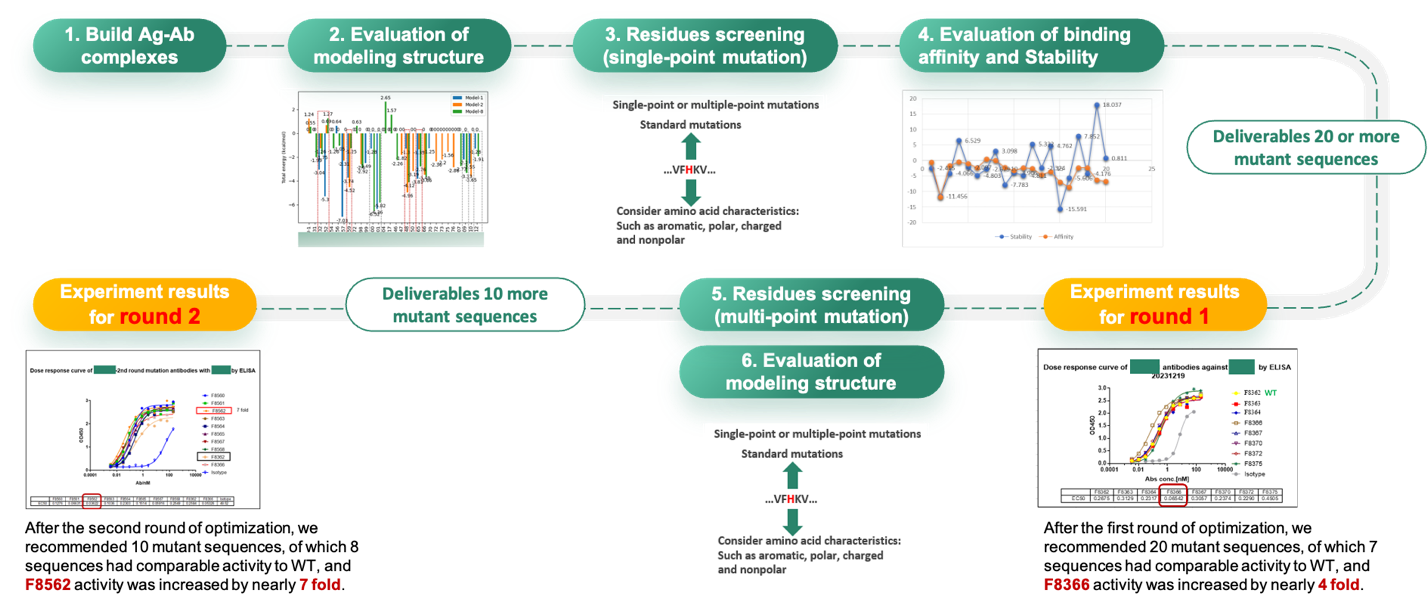
Case Study: antibody affinity maturation through dry-lab and wet-lab integration
De novo design: bringing unprecedented imagination to drug design
The idea of de novo design was proposed decades ago in the field of computational chemistry. Recent advancements in generative AI that materialized the concept into practical applications. This approach enables the direct generation of novel molecules complementary to the targets without conventional screening thereby escaping the chemical-space boundary of the compound libraries. When combined with FEP for lead optimization, it can accelerate the R&D process by orders of magnitude. Viva Biotech's computational platform integrates de novo design with experimental validations at all stages, from synthetic accessibility (SA) to drug-likeness of the compounds. The figure below shows an overlay of the de novo designed molecule (pink) and the crystal structure ligand (green) in the binding pocket, where similar binding mode is achieved by novel chemical matters.
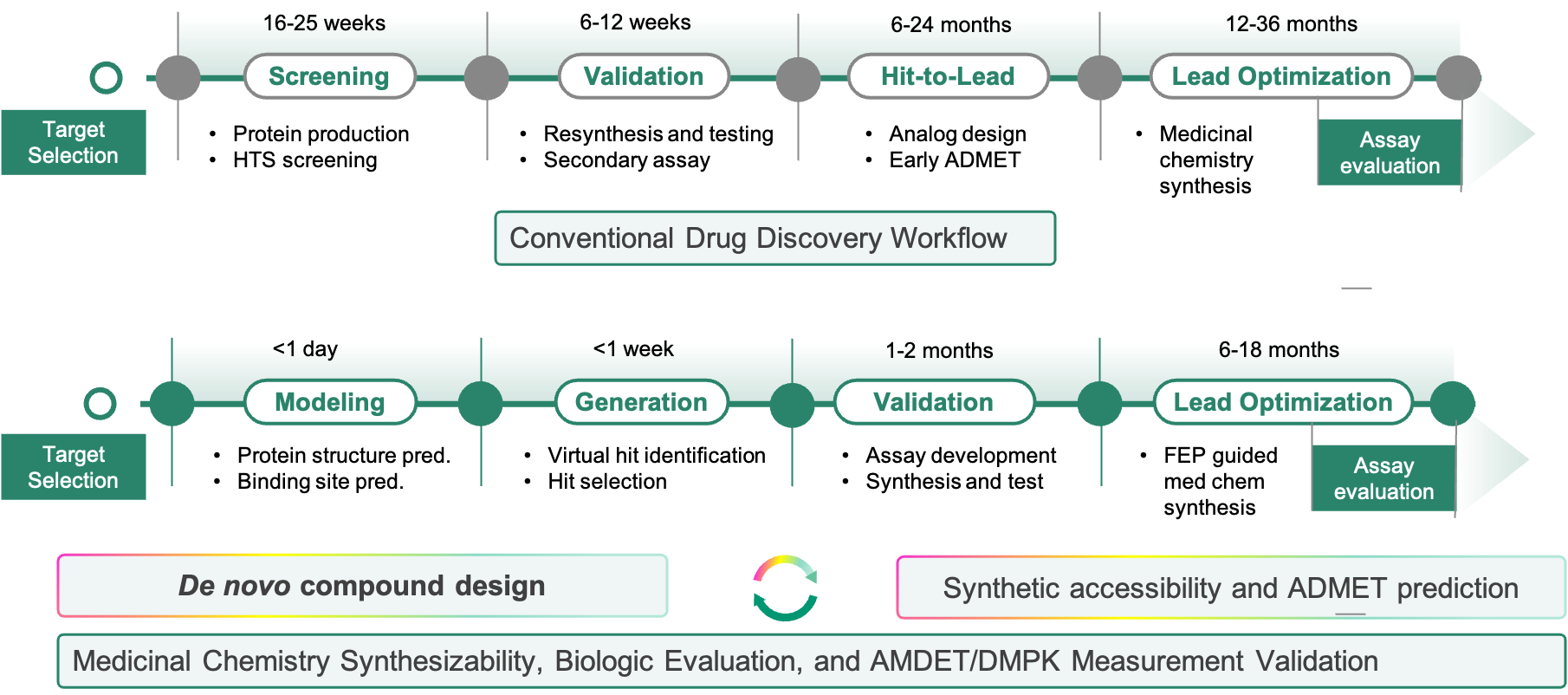
A comparison of the traditional drug design process and the de novo design process
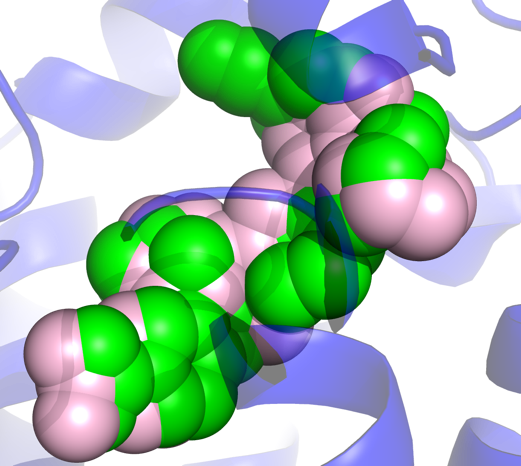
An overlap of de novo designed molecule (pink) and the crystal structure ligand (green)
Viva Biotech excels in AI-driven drug discovery for small molecules, RNA-targeting small molecules, peptides/cyclic peptides, and antibody drugs, leveraging advanced physics-based models and AI algorithms. Powered by the supercomputing clusters, Viva applies these cutting-edge algorithms at every drug discovery stage and actively explores the potential of de novo design. With a team consisting mainly of experts holding doctoral degrees, Viva Biotech stays at the forefront of drug design. The AIDD and CADD platform is dedicated to developing widely applicable methods while overcoming scientific challenges for various drug modalities. As the algorithms are continued to be improved and the high-quality data accumulated, we believe this revolutionary technology will change how we think and execute in developing new drugs.

